
By W. Jack. Southwestern University School of Law. 2018.
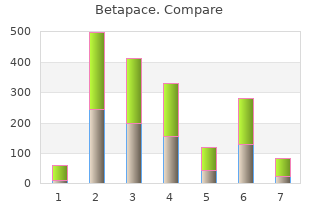
Leurs purchase 40 mg betapace with amex heart attack vol 1 pt 3, R purchase betapace 40mg blood pressure chart bhf, Blandina, P, Tedford, C and Timmerman, H (1998) Therapeutic potential of histamine H3 receptor agonists and antagonists. Rupprecht R and Holsboer F (1999) Neuroactive steroids: mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological perspectives. Tohyama, M, Tamiya, R, Inagok, N and Takagi, H (1991) Morphology of histaminergic neurons with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Needless to say, any change observed must only be found in patients with that disorder and it must not be a consequence of drug therapy, diet or other identifiable factors. Even then it is still necessary to establish whether the change causes the disorder or results from it. The objective is clearly demanding and yet the methodology to realise it is often unreliable. For these reasons much attention has been focused on the monoamines since despite uptake and re-use their metabolites can be measured in blood and urine, even if their origin is not easily established. If plasma concentrations are of little value then analysis of the urine is even more pointless. The value of direct studies on brain tissue itself depends to some extent on whether the disorder has a distinct neuronal lesion or just a biochemical malfunction with no clear neuronal degeneration. In psychiatric disorders there is no clear neurodegeneration and the assumed bio- chemical fault has been even more difficult to identify. This measures the distribution of a previously administered positron-emitting isotope. The positron emitted from the proton of the isotope collides with an electron in the atomic orbit so that two gamma-rays are given out simultaneously at 1808 to each other. The intensity of the detected emission is colour coded and reflects the concentration of ligand (Fig. Of course, a low level of emission will be detected throughout the brain from the presence of the labelled substance and its metabolites in the blood and extracellular fluid, as well as that non-specifically located in all neuronal and glial tissue and such background activity must be distinguished from the more specific labelling. After its injection a labelled precursor should be taken up and detected in appropriate nerve terminals (and possibly cell bodies) so that the intensity of emission reflects the density of nerve terminals and the innervation. Using this procedure it has been possible to show that very little [18F] fluorodopa is concentrated in the striatum of Parkinsonian patients, compared with normals (Fig. The injection and subsequent detection of an appropriately labelled ligand can give an indication of the density of the receptors to which it is bound. As with any binding study the validity of the approach depends on the specificity of the ligand for its receptor. The difference between these two levels should in fact increase as unbound drug is lost (excreted). To determine the precise number of receptors and see if that varies from brain to brain (e. Normally the estimation of receptor number requires a measure of specific binding at two or more ligand concentrations under equilibrium conditions (see Chapter 3), which will clearly be difficult in vivo, not least because the effect of different doses may be unacceptable to the patient or subject. It must also be remembered that much of the in vivo binding can be to presynaptic receptors and uptake sites as well as postsynaptic receptors, although drugs specific for those sites can be used to label nerve terminals. Good correlations between the analgesic potency of morphine derivatives and displacement of the labelled morphine antagonist, naloxone, helped not only to formulate the concept of opioid receptors and hence of endogenous opioids to occupy them but also the actual discovery of the enkephalins. Displacement of labelled diazepam by a wide range of other benzodiazepines, in an order in keeping with their clinical efficiency as anxiolytics, led to the realisation of endogenous benzodiazepine receptors.
This view was partly based on findings in enzymology buy betapace 40 mg lowest price blood pressure medication ending in pine, in which this concept is generally valid for metabolite–antimetabolite competition as well as for activity studies of vitamins and hormones purchase betapace 40mg visa pulse pressure of 80. An antimetabolite is a molecular analog of an intermediate in a physiologically relevant metabolic path- way that replaces a natural substrate. In doing so, it prevents the biosynthesis of phys- iologically important substances within the organism. The close structural resemblance of agonists and antagonists in these categories constitutes direct proof that they have identical binding sites. The lack of structural correlations between many neurotrans- mitters and their blocking agents, however, initiated a review of the competitive bind- ing hypothesis. It is generally accepted that there is complementarity between a ligand (either endogenous [e. Under optimal conditions, the energies liberated in binding can reach 40–50 kJ/mol, a figure equivalent to binding equilibrium constants of about 10–8–10–9, which is considered to represent a high affinity. Complementarity in the context of induced fit implies a plasticity of the receptor macromolecule in terms of an ability to undergo conformational changes and associate with ligands. For stereospecific binding, it is generally assumed that a ligand must have three unequal substituents; this is considered sufficient for great selectivity. The discrete forms of a receptor site are, of course, the result of receptor plasticity. Recognizing this capacity of the receptor to assume different molecular geometries without a significant change in function is probably essential to achieving some under- standing of the pluralistic nature of many receptors. It is physiologically and struc- turally unreasonable to assume that a given type of receptor—probably a complex, multisubunit structure that is part of an even more complex membrane framework—is absolutely identical throughout an organism. Mautner pointed out in 1967, long before the structure of any drug receptor was known in any detail, that the medicinal chemist would have to deal with an isoreceptor concept in the same matter-of-fact way that an enzymologist accepts isozymes. Despite recent advances in molecular biology, our present knowledge of receptor structure is still evolving. Consider, for example, the presence of opiate receptors in both the central nervous system and the ileum. In the first case, the receptor modulates neurotransmitter release; in the second, it may activate an enzyme such as adenylate cyclase, or trigger an action poten- tial. As we shall see later, almost all neurotransmitters show receptor multiplicity, and medicinal chemists deal with multiple adrenergic receptor subtypes and many different opiate receptors, just to name two examples. Receptor plasticity could be invoked as the underlying common trait of multiple receptors. For example, although the multiple adrenergic isoreceptors are similar, they react to the common neurotransmitter norepinephrine (2. They also show a drug specificity that varies from organ to organ and differs in various species of animals. In subsequent chapters of this book, receptor multiplicity as the rule rather than the exception will become amply evident. It is to be hoped that, in time, the comparison of isoreceptor molecular structures will provide precise criteria for their differentiation. The multiplicity of receptor or recognition sites for agonists and antagonists is well documented. One may distinguish (i) agonist binding sites, (ii) competitive antagonist binding sites (accessory sites), and (iii) noncompetitive antagonist or regulatory bind- ing sites (allosteric sites).
The extent to which any of these receptor interactions affects the efficacy of these compounds is not known order 40mg betapace amex blood pressure chart by age. It is hoped that this approach might increase the response rate of patients who are resistant to more selective drug treatments and even reduce the therapeutic lag that dogs their predecessors buy betapace 40mg cheap prehypertension and hypertension. As yet, there is not enough information on these compounds to know whether or not this has turned out to be the case. These are triazolopyridine derivatives and include trazodone and the more recent addition, nefazodone. A related compound that has recently been introduced into the clinic is nefazodone. It has a lower affinity for the receptors that are responsible for the unwanted side-effects of trazodone, in particular a1-adrenoceptors and muscarinic receptors. Ultimately, agonist drugs that directly activate monoamine receptors would appear to be a logical development in this field. Unfortunately, the peripheral side-effects of such compounds could well limit their acceptability even if we were to discover what subset of receptors to target. Yet an outstanding problem in treating depression is that the therapeutic response is both slow and progressive: a significant improvement usually takes at least 2±3 weeks and sometimes much longer. Obviously, if we are to explain the therapeutic effects of antidepressants, we must search for long-term neurochemical changes that occur after their prolonged administration. They found that repeated, but not a single, administration to rats of any of the antidepressants which were available at that time (i. Shortly afterwards, it was found that this desensitisation was usually paralleled by downregulation of b1-(butnotb2-) adrenoceptors. This action is even shared by repeated electroconvulsive shock(Stanford and Nutt 1982) but not by drugs that are ineffective in relieving depression (e. A logical conclusion from this workwas that depression is caused by hyperresponsive b-adrenoceptors. However, proliferation of receptors is the normal response to a deficit in transmitter release and so the opposite change, downregulation of b-adrenoceptors by antidepressants, would follow an increase in the concentration of synaptic noradrenaline. This would be consistent with both their proposed mechanism of action and the monoamine theory for depression. Nonetheless, there are many reasons to be confident that b-adrenoceptor desensitisa- tion does not explain the therapeutic effects of antidepressants. First, with the development of more selective ligands for use in radioligand binding studies, it became evident that b-adrenoceptor downregulation can occur after only 2±3 days of drug treatment (Heal et al. Evidently, we must lookelsewhere to find an explanation for the neurobiology of depression and its treatment. Indeed, apart from developing compounds that help patients who currently do not respond to any existing treatment, the most pressing problem in this field is to reduce the delay in treatment response. Yet, despite the numerous investigations of the effects of antidepressants on a wide range of transmitter receptors, few consistent findings have emerged. Results tend to vary not only from laboratory to laboratory and between different brain regions but they also vary with the species and compound tested. So far, the neurochemical changes induced by long-term drug treatment have not been tested in combination with procedures such as learned helplessness, but it cannot be assumed that they will be the same as those in normal (non-depressed) subjects. Some studies find reduction in locus coeruleus, only b-adrenoceptor binding (cortex) 1-adrenoceptors, only. This suggests that depression is associated with a defect in the regulation of glucocorticoid secretion and the locus of this disorder could be glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus. Since this happens even in cultured fibroblasts it is thought to involve an action at the level of the genome.
When you’re experiencing too After a trigger point has healed trusted 40mg betapace blood pressure chart bpm, that area of the muscle much stress cheap betapace 40mg mastercard arrhythmia occurs when, you tend to tense your muscles (reducing blood tends to have a good memory. The trigger point has circulation in those muscles), drink too little water (reducing “branded” it, so to speak, so the next time you experience the blood volume available to clear out toxins in the muscles), stress, overwork certain muscles, or fail to drink enough eat too much unhealthy food (causing inflammation that water, that muscle can contract again in the same place, makes trigger points swell), and forget to move around and activating the same trigger point as before. Let’s say that one day you These behaviors lead to shallow breathing, which delivers accidentally drop it and break the handle. But that handle lead to decreased blood flow—that stagnation or “too slow” now has an old old injury. Without adequate blood flow, the muscle cells in the Trigger points act the same way, particularly if they aren’t trigger-point areas of your body are unable to activate the healed completely. They tend to return again and again, relaxation response that makes the trigger point disappear or whenever the body is under stress. The mechanism that allows muscle cells adopt healing solutions and lifestyle habits that keep trigger to “let go” requires the oxygen and energy provided by good points relaxed and dormant—and keep new ones from blood circulation. Trigger points also can occur as a result of muscle trauma (from car accidents, falls, sports- and work-related injuries, Trigger Points and “Referred” Pain etc. Unfortunately, once you beyond the pain you’re experiencing so you can address the have a trigger point, it tends to undergo a self-reinforcing cause of that pain. Here’s another reason why: Trigger points cycle—which means it sticks around for a while. It’s as if the trigger point Active and Inactive Trigger Points “refers” its pain to some other muscle or area of the body, saying, “Here, you take this message to the brain. Just the For example, you could be feeling pain in your hips, stresses of living can create them in our bodies over time. Trigger points also can refer pain to other trigger points along the same nerve pathways. So, if your health practitioner is not educated in seeking out the cause of the pain, she may simply focus on the location of that pain—your legs, for example—while ignoring the fact that the trigger point in your lower back is causing it. That’s unfortunate, because then any treatments she implements will only partially (if at all) help the condition. Any treatment that fails to address your shoulder problem is going to be unsuccessful. Therefore, it’s important to find the trigger points, wherever they are, and heal them, one by one. Trigger-point therapy is a method by which steady, sustained pressure is applied to the “knotted” area. Such pressure gradually encourages the muscle fibers to relax and release, loosening the twisted places. Since muscles that have trigger points are typically too tight and too short, trigger- point therapy encourages elongation and relaxation. As the fibers return to a more healthy shape, they let loose all the pent-up toxins that had been trapped there, returning them to the bloodstream where they can be washed away. Eventually, muscle spasms disappear, tenseness goes away, and the muscle returns to more normal function. This process also creates an overall body release, or “sigh of relief,” reducing the pain signals to the brain and alerting your system to restore itself.
SHARE THE DANA LANDSCAPING PAGE